High Grade Vs Low Grade Glioma Radiology
For a general discussion see glioma treatment response. High-grade tumors as well as low-grade mixed gliomas tumors that contained classic biphasic oligoastrocytomas were excluded from the study.

Texture Description Of Low Grade And High Grade Glioma Using Statistical Features In Brain Mris Semantic Scholar
Higher grade gliomas typically demonstrate heterogeneous tissue texture and signal intensity on TI.
High grade vs low grade glioma radiology. Response assessment in neuro-oncology criteria RANO published in 2010 1 are used to assess response to first-line treatment of glioblastoma as well as lower grade astrocytoma 3 and have largely superseded the older Macdonald criteria which only dealt with glioblastoma multiforme 2. The 10th percentile of the heterogeneity index was significantly lower. The mean volume transfer constant K trans and volume of extravascular extracellular space v e derived using arterial input functions AIFs at dynamic susceptibility-contrast DSC MR imaging were more accurate for differentiating high-grade from low-grade astrocytoma than those derived using AIFs from dynamic contrast-enhanced DCE MR. Low-grade gliomas LGGs are a heterogeneous group of tumors. It has often especially in older literature been used to denote both anaplastic gliomas WHO grade III and glioblastomas WHO grade IV always including astrocytomas but variably also including oligodendrogliomas. Pathology reports of the imaging results were reviewed independently.
However treatment can be very effective for low-grade glioma. - 018 063 068 074 vs. Two neuropathologists AB TT separately reviewed all the slides from each patient without knowledge of. The distinction between high-risk and low-risk patients with low-grade glioma is far from clear. Under a microscope a low-grade glioma more closely resembles normal tissue than a high-grade glioma and it also grows and spreads more slowly. A glioma can be described as either low grade or high grade.
The World Health Organization WHO classification system categorizes gliomas from grade 1 lowest grade through grade 4 highest grade based upon histopathologic characteristics such as cytological atypia anaplasia mitotic. High-grade glioma is a relatively vague term and in some ways is best avoided unless one deliberately wants to be vagueinclusive. In low-grade gliomas rCBV and rCBF ratios were 169-051 and 116-038 respectively. Table 2 summarizes the differences in the APT ADC and rCBV values between low- and high-grade gliomas. The MR spectrum of more infiltrative malignant and high-grade tumors overlaps those of lower grade lesions but generally the features are different. The skewness of the apparent diffusion true-diffusion and distributed-diffusion coefficients was significantly higher in high-grade than in low-grade gliomas 067 067 vs.
- 015 073. Grade 3 and 4 gliomas are considered high-grade. - 008 066 063 072 vs. The rCBV and rCBF ratios for high-grade gliomas were statistically different from those of low-grade gliomas p 0001. Low-grade gliomas grow very slowly but are still malignant and can progress to high-grade gliomas if left untreated. A receiver operator curve ROC analysis assessed the predictive potential of cMRI and ADC values for low-grade and high-grade gliomas.
Up to 10 cash back ROC analyses and added value of APT imaging. Doctors Work with You to Choose the Treatment that Best Suits Your Needs. For peripherally enhancing masses the main differential diagnosis lies between high-grade and secondary brain tumours inflammatory or demyelinating lesions and abscesses. Their cells are undifferentiated and highly malignant and have a worse prognosis. Grade II and high-grade gliomas HGGs. The current evidence indicates that after resection of the tumor high-risk patients benefit from immediate.
The APT and rCBV values were significantly higher and the ADC values were significantly lower in high-grade gliomas than they were in low-grade gliomas all P 0001. Yet this criterion is used to select patients for immediate postsurgery radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Contrast enhancement in tumor may suggest impaired blood brain barrier with leakage of contrast agents into the. P 00066 00192 and 00128 respectively. Gliomas classified as grades 1 and 2 are termed low-grade because their cells are well-differentiated exhibit less aggressive tendencies and have a better prognosis. Nevertheless the sensitivity and specificity of existing MRI protocols are limited According to the WHO classification grade II gliomas also called low-grade gliomas LGG express atypical nuclei and inevitably progress at a rate that varies from.
At present MRI is the first line imaging technique for the non-invasive exploration of intracranial tumor progression. Oncologists often use the terms low-grade and high-grade to categorize malignant gliomas based on how quickly the tumors spread. Gliomas are the most common primary neoplasms of the brain varying histologically from low grade to high grade in World Health Organization WHO classification. 1 The differentiation between low-grade gliomas LGGs. Fifty-six subjects met the inclusion criteria. A value of rCBV greater than 2 showed a sensitivity of 90 and specificity of 67 and rCBF greater than 14 showed a sensitivity of 100 and a specificity of 74 in discrimination of high grade gliomas versus low grade gliomasPWMRI is more accurate than conventional MRI for noninvasive discrimination of low-grade glioma LGG and high-grade.
The combination of MRI and ADC values increased sensitivity to 90 and negative predictive value to 929 and also. Non-enhancing lesions may represent low-grade gliomas LGGs viral encephalitis and developmental anomalies such as focal cortical dysplasia. Nonetheless low-grade gliomas usually show no increase in tumor rCBV Figure 8 while high-grade gliomas may demonstrate high rCBV that in some cases extends outside the contrast-enhancing portion of the tumor Figure 9. In high-grade gliomas rCBV and rCBF ratios were measured as 650-429 and 332-187 mean-SD respectively. Grades III IV is critical since the prognosis and thus the therapeutic strategy could differ. Ad Offering a Full Range of the Latest Treatments for Glioma.
Many low-grade gliomas demonstrate little or no contrast enhancement similar to the temporal lobe mass in this patient.

Low Grade Gliomas The Challenges Of Imaging Sciencedirect
Mri Features May Predict Molecular Features Of Glioblastoma In Isocitrate Dehydrogenase Wild Type Lower Grade Gliomas American Journal Of Neuroradiology
Response Assessment In Neuro Oncology Criteria For Gliomas Practical Approach Using Conventional And Advanced Techniques American Journal Of Neuroradiology
Low Grade Glioma Correlation Of Short Echo Time 1h Mr Spectroscopy With 23na Mr Imaging American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Low Grade Glioma Mri Operative Neurosurgery

Typical Mri Scan Of A Low Grade Glioma Histopathologically Defined As Download Scientific Diagram
3 0t Imaging Of Brain Gliomas Radiology Key
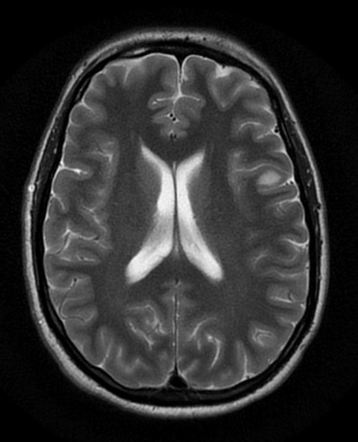
Left Frontal Low Grade Glioma Radiology Case Radiopaedia Org
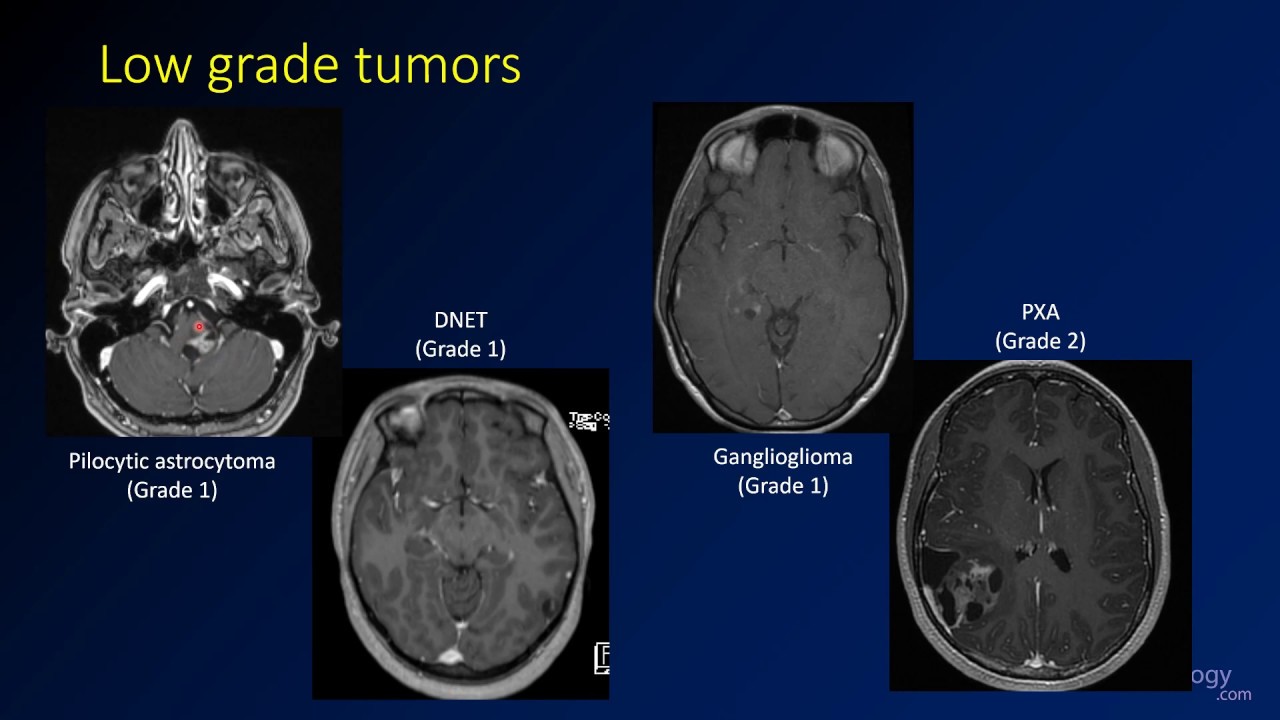
Imaging Brain Tumors 4 Other Low Grade Gliomas Youtube

High Risk Low Grade Glioma Neurosurgery
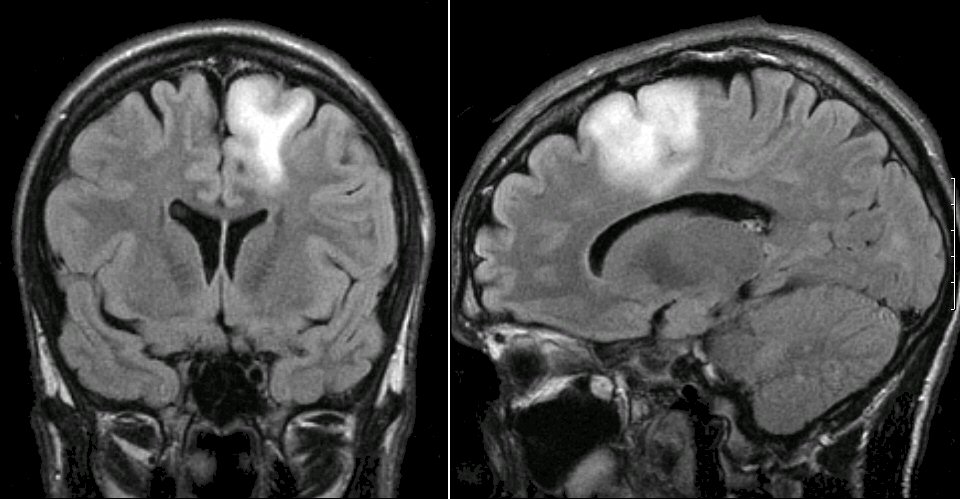
Posting Komentar untuk "High Grade Vs Low Grade Glioma Radiology"