Internal Carotid Artery Compression Symptoms
Internal bleeding in the brain may cause minimal damage or it may lead to stroke-like symptoms coma and death. CCFs are classified based on the arterial.

Symptoms And Conditions Of Cervical Spine Compression Causing Internal Jugular Vein Stenosis Caring Medical Florida
This is one of two arterial circuits the other being the anterior circulation that delivers up to 15 of the total cardiac output to the brain tissueThis high demand for oxygenated blood is based on the.

Internal carotid artery compression symptoms. Brief Reports and Innovations is a gold open access journal launched by Annals of Vascular Surgery. 11th Annual Cerebrovascular Symposium May 11-12. In medicine a pulse represents the tactile arterial palpation of the cardiac cycle heartbeat by trained fingertips. Multiple connections to other key vessels including ophthalmic internal carotid MHT ILT ascending pharyngeal occipital these can be. Computed tomography angiography demonstrated a 114 77 8-cm pseudoaneurysm at the base of the right neck which had arisen from the right subclavian artery and extended into the right superior mediastinum producing significant compression of the right common carotid artery with a tracheal mass effect. The acoustic neuroma is the most common tumor of the cerebellopontine angle.
A doctor will perform this surgery to restore normal blood flow to the brain to prevent a stroke if a person. This compression decreases flow through the circle of Willis with intensification and prolongation of an internal carotid bruit and diminution of an external carotid murmur see Table 181 for summary. AMA PRA Category 1 CME credit for Clinical Imaging reviewers. Large aneurysms are at risk for rupture bursting. The main symptoms are chronic abdominal pain. Internal Carotid Arteries.
Symptoms depend upon the location of the bleeding the amount of bleeding and whether the bleeding causes increased pressure within. The mission of The Annals of Thoracic Surgery is to promote scholarship in cardiothoracic surgery patient care clinical practice research education and policy. A carotid-cavernous fistula may be either direct high-flow or spontaneous indirectlow flow. Superior mesenteric artery SMA syndrome is a gastro-vascular disorder in which the third and final portion of the duodenum is compressed between the abdominal aorta AA and the overlying superior mesenteric arteryThis rare potentially life-threatening syndrome is typically caused by an angle of 625 between the AA and the SMA in comparison to the normal range of. When iliac artery aneurysms increase in size they may cause symptoms such as compression of adjacent structures. This is a risk factor for stroke.
With an aneurysm the artery expands like a balloon. The carotid artery is usually palpated near the lateral side of the sternal head of the sternocleidomastoid and the internal jugular vein usually lies superficial and lateral often minimally lateral to the carotid artery. If the wall of the carotid artery is weak an aneurysm can form. Usual origin from the proximal Internal Maxillary Artery IMAX with multiple clinically-important variants. New Journal Launched. Least sensitive study unable to adequately evaluate vertebral arteries or proximal internal carotid No LOC anoxic brain injury No visual changes.
Carotid bruits are detected in 4 to 5 of the population aged 48 to 80 years and are associated with internal carotid artery stenosis in 50 of cases. The association between carotid intima-media thickness and cognitive performance is affected by intracranial artery stenosis in Chinese elderly people. Carotid-cavernous fistula CCF is an abnormal connection between the carotid artery andor its branches and a large vein called the cavernous sinus. The EOCME is accredited by the Accreditation Council for. If the aneurysm grows large enough it can rupture burst or have clot that builds up break off and go to the brain and cause strokes. As the official journal of two of the largest American associations in its specialty this leading monthly enjoys outstanding editorial leadership and maintains rigorous selection standards.
Acoustic neuromas vestibular schwannomas are benign Schwann cell tumors that typically arise from the vestibular portion of the eighth cranial nerve. Clots may develop in aneurysms that can obstruct the vessel or can break off and obstruct smaller arteries in the extremities. Other causes of carotid bruits include increased venous flow external carotid artery stenosis and transmitted cardiac murmur. Carotid artery stenosis which is a narrowing of the carotid arteries due to a buildup of plaque inside them. The internal carotid arteries ICA originate at the bifurcation of the left and right common carotid arteries at the level of the fourth cervical vertebrae C4. This is a major risk factor for stroke.
A carotid-cavernous fistula CCF is the result of an abnormal vascular connection between the internal carotid artery ICA or external carotid artery ECA and the venous channels of the cavernous sinus. It can slow blood flow or dangerously weaken the wall of the artery. They do not supply any branches to the face. With an aneurysm the artery expands like a balloon. The basilar artery is a relatively large robust blood vessel located in the posterior cranial fossa. Carotid artery dissection which is a split in the layers of the carotid artery wall.
2016 3 Post-op Carotid Management Objectives Review the potential complications of carotid surgery Cranial nerve palsies Hemodynamic instability Hyperperfusion syndrome Stroke MI Post op neck hematoma Discuss the clinical management of these complications when applicable. The new surgical journal seeks high-quality case reports small case series novel techniques and innovations in all aspects of vascular disease including arterial and venous pathology trauma arteriovenous. Spots flashing light tunnel vision. The cavernous sinus is located behind the eye and receives blood from brain orbit and pituitary gland. Carotid artery surgery also. They move superiorly within the carotid sheath and enter the brain via the carotid canal of the temporal bone.
The Editors of Clinical Imaging in conjunction with the Elsevier Office of Continuing Medical Education are pleased to offer an AMA PRA Category 1 CME credit program for registered Clinical Imaging physician reviewers who complete manuscript reviews. Celiac artery compression syndrome also known as median arcuate ligament syndrome is a condition where a muscular fibrous band of the diaphragm the median arcuate ligament compresses the celiac axis which supplies blood to the upper abdominal organs. The most common presenting symptoms are unilateral sensorineural hearing loss tinnitus and imbalance. Injury stroke symptoms and intercerebral petechial hemorrhage Carotid Doppler Ultrasound NOT RECOMMENDED. Tortuosity and redundancy of the internal carotid artery is a common angiographic and MR angiographic finding 1 2 9In one of the largest angiographic studies conducted by Weibel and Fields internal carotid artery tortuosity and angulation respectively were observed in 35 and 5 of 1438 consecutive patientsTortuous vertebral subclavian and lingual arteries. The pulse may be palpated in any place that allows an artery to be compressed near the surface of the body such as at the neck carotid artery wrist radial artery at the groin femoral artery behind the knee popliteal artery near the ankle joint posterior tibial.
Internal carotid outflow also increases with careful compression of the contralateral common carotid artery during auscultation. However variant orientation of these vessels occurs regularly in 9 to 19 of patients. Annals of Vascular Surgery. It is the main blood vessel that forms the posterior circulation of the brain.
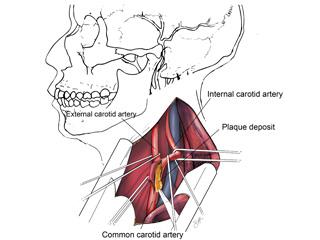
Carotid Artery Disease Baylor Medicine
Narrowing Of The Carotid Arteries May Lead To Memory And Thinking Problems

A Rare And Subtle Etiology Of Chronic Oropharyngeal Pain Isolated Internal Carotid Artery Kinking Without Stenosis Annals Of Vascular Surgery

Carotid Artery Compression Of The Optic Nerve Ophthalmology

Symptoms And Conditions Of Cervical Spine Compression Causing Internal Jugular Vein Stenosis Caring Medical Florida
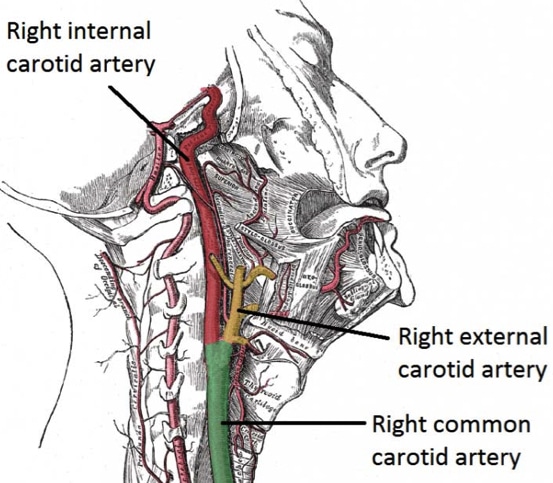
Carotid Artery Disease Clinical Features Management Teachmesurgery
Reversible Left Hemispheric Ischemia Secondary To Carotid Compression In Eagle Syndrome Surgical And Ct Angiographic Correlation American Journal Of Neuroradiology

Treating Neurologic Like Symptoms By Addressing Cervical Spine Instability And Disrupted Blood Flow Into The Brain Caring Medical Florida

Bilateral Eagle Syndrome With Associated Internal Carotid Artery Kinking And Significant Stenosis Annals Of Vascular Surgery

Symptoms And Conditions Of Cervical Spine Compression Causing Internal Jugular Vein Stenosis Caring Medical Florida

Symptomatic Compression Of The Optic Nerve By The Carotid Artery Ophthalmology

Figure 2 From Recurrent Syncope Caused By Compression Of Internal Carotid Artery By An Anomalous Hyoid Bone Semantic Scholar

Posting Komentar untuk "Internal Carotid Artery Compression Symptoms"